As the number of fiber optic interfaces is growing, third-party optical modules have become significantly more popular due to their attractive price, which reduces expenses of your network.
However, only good-quality modules reduce your costs instead of increasing them.
Off-brand transceivers are often said to cause compatibility issues with active devices such as switches, servers, or routers. The reason for these problems is that vendors of active devices block the possibility of using modules not produced by them. In order to protect their revenues from sales of their modules, they constantly modify and update the software of their devices so that it supports only their own transceivers.
Is it beneficial to use third-party transceivers?
It may happen that an unoriginal optical module is not recognized by the device in which it is supposed to work, or it is recognized initially, but after software updates it stops working with the device in which it is installed.
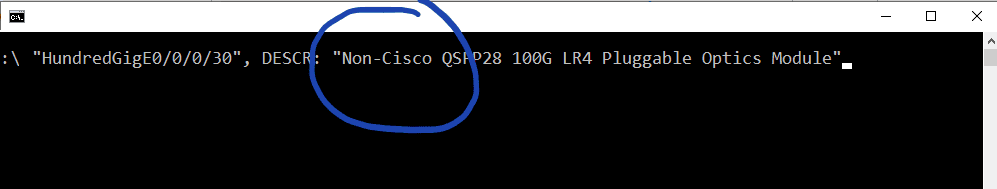
This situation raises many problems: unoperating links, dissatisfaction of clients, incurring additional costs associated with the replacement of the module, and the working hours of someone who will dismantle it and reinstall the link. We must send the defective transceiver back to the supplier or producer, wait for its return or replacement, reinstall it, and provide the client with a replacement link. Additionally, if the module's warranty has expired, we must buy a new one or pay for its reprogramming.
The problems and costs begin to pile up, and the initially low cost of off-brand modules increases significantly. We pay an employee to do the installation work, and a trucking company to deliver the module to the supplier/manufacturer. It also happens that as compensation for the non-functioning link, we have to reduce the subscription fees of customers or pay contractual penalties for service interruptions. Sometimes we are forced to buy another module or look for another provider, which we have neither time nor inclination for.
It doesn't have to be this way!
The compatibility of the transceiver is influenced not only by the way it is programmed but also by the repeatability of the PCB production. It translates directly into compatibility of the optical module with the active device, in which it is installed. Unfortunately, it often happens that manufacturers of optical modules do not pay attention to changes in PCB designs. Lack of such repeatability causes the module to be unidentifiable by the switch or router or leads to malfunctions.
A perfect solution for compatibility issues would be to program the transceiver on your own, at any place or time. Some of you may have heard about the possibility to program the transceivers at home. But is it really so easy and hassle-free?
POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS:
- An optical module of a certain type reports as a different type. Is it an error?
In some situations, the transceiver is recognized by the switch, and transmission runs without any problems, but the module itself is marked in the device as a different type. For example, we install a BiDi module, which is reported in the switch as a different type, such as "LR". This type of situation usually occurs when the manufacturer of the active device, such as a switch, does not have a BiDi module in their offer. Thus, for such a module to be recognized by this switch, it must be programmed as one of the transceiver types available from such a manufacturer, e.g., "LR". In this case, although the module shows as a different type, it is not incorrectly programmed, because the transmission itself is correct, and the switch recognizes it.
- We have a correctly programmed optical module, but the link does not pick up. What to do now?
Some compatibility issues can be easily solved by following the steps given below:
To activate the link manually and configure the port:
- check if the module is correctly inserted
- by running the DDM diagnostics check whether the TX diode/laser transmits the signal and the RX diode receives it correctly
- check whether the optical connectors of the module and patch cable are clean
- check the port’s settings (speed, FEC)
- if the link does not activate, manually set the data speed
- if the link is activated, but the transmission is unstable, check the port’s settings (VLAN and routing)















