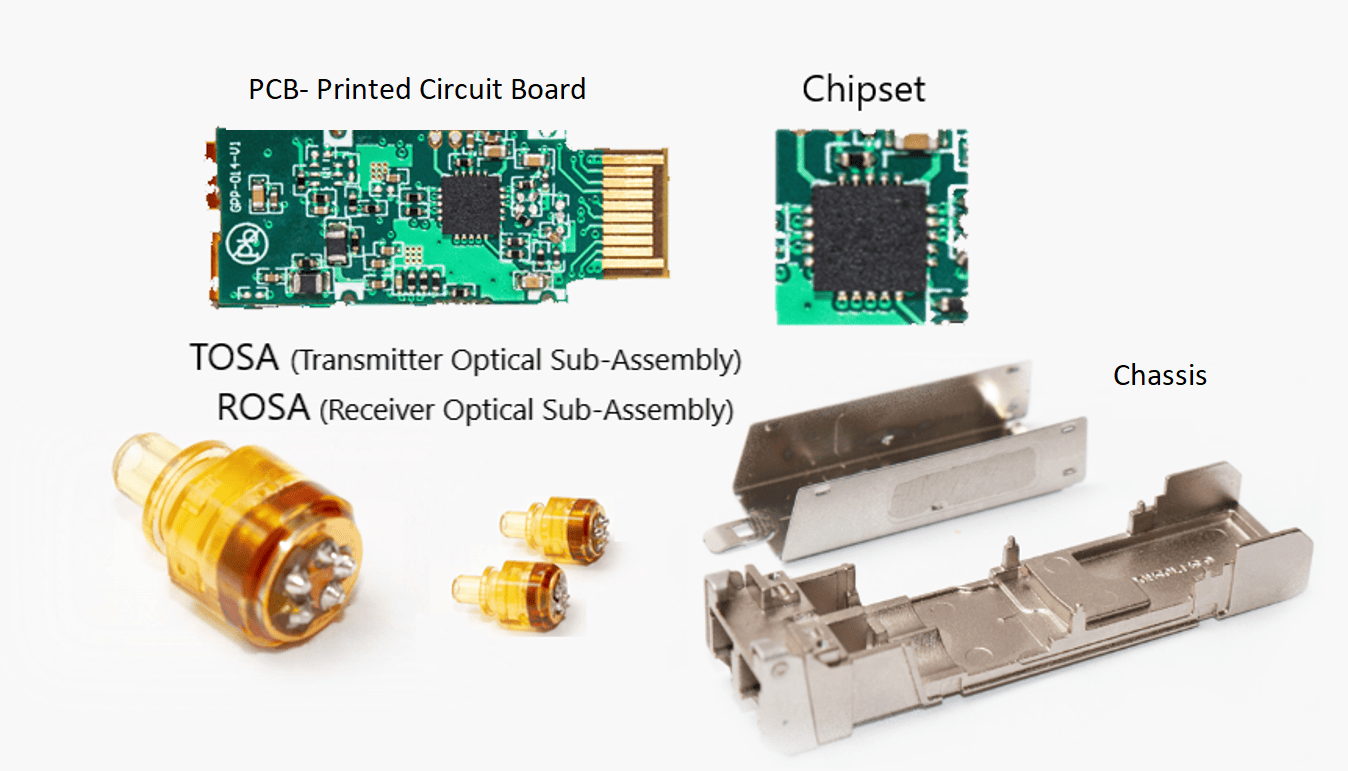
The SFP module enables fiber-optic transmission between network devices such as switches, routers, server cards, or media converters. The SFP module (also known as SFP transceiver or Mini-GBIC) is an optical module that converts optical signals to electrical and vice versa. In simple terms, the SFP module consists of:
Components of an optical transceiver
- A light source, namely a TX transmitter, which can be either a laser or a diode, that transmits the fiber optic signal
- An RX receiver (a receptive diode) that detects the fiber-optic signal and converts it to electrical
- A PCB board – an integrated circuit with a chipset
SFP PORT – APLICATION
The SFP port is a fiber-optic interface used in network devices such as switches, routers, server cards, and media converters for fiber-optic signal transmission through cabling.
Copper cables have a limited range and capacity, so the more popular choice is fiber-optic interfaces that enable data transmission capacity of 1G and data transmission of up to 400 Gbs. The most common SFP modules are SFP 1 Gbs, SFP+ 10 Gbs, XFP 10 Gbs, SFP28 25 Gbs, QSFP+ 40 Gbs, QSFP28 100 Gbs, CFP, QSFP-DD 400 Gbs.
SFP+ AND FIBEROPTIC INTERFACES – ADVANTAGES
What are the advantages of fiber-optic interfaces?
- Higher data transmission speed
- Wider range
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference
- Low latency
- Reliability
SFP MODULES – TYPES
SFP modules can be categorized based on the type of optical fiber, wavelength, and transmission range.

For different types of fibers, you will need different transceivers. For your convenience, the transceivers are color-coded by the manufacturers on the transceiver’s bale clasp/latch, as shown above. These clasps are used to safely remove the transceiver from the fiber-optic port on the switch, converter or server.
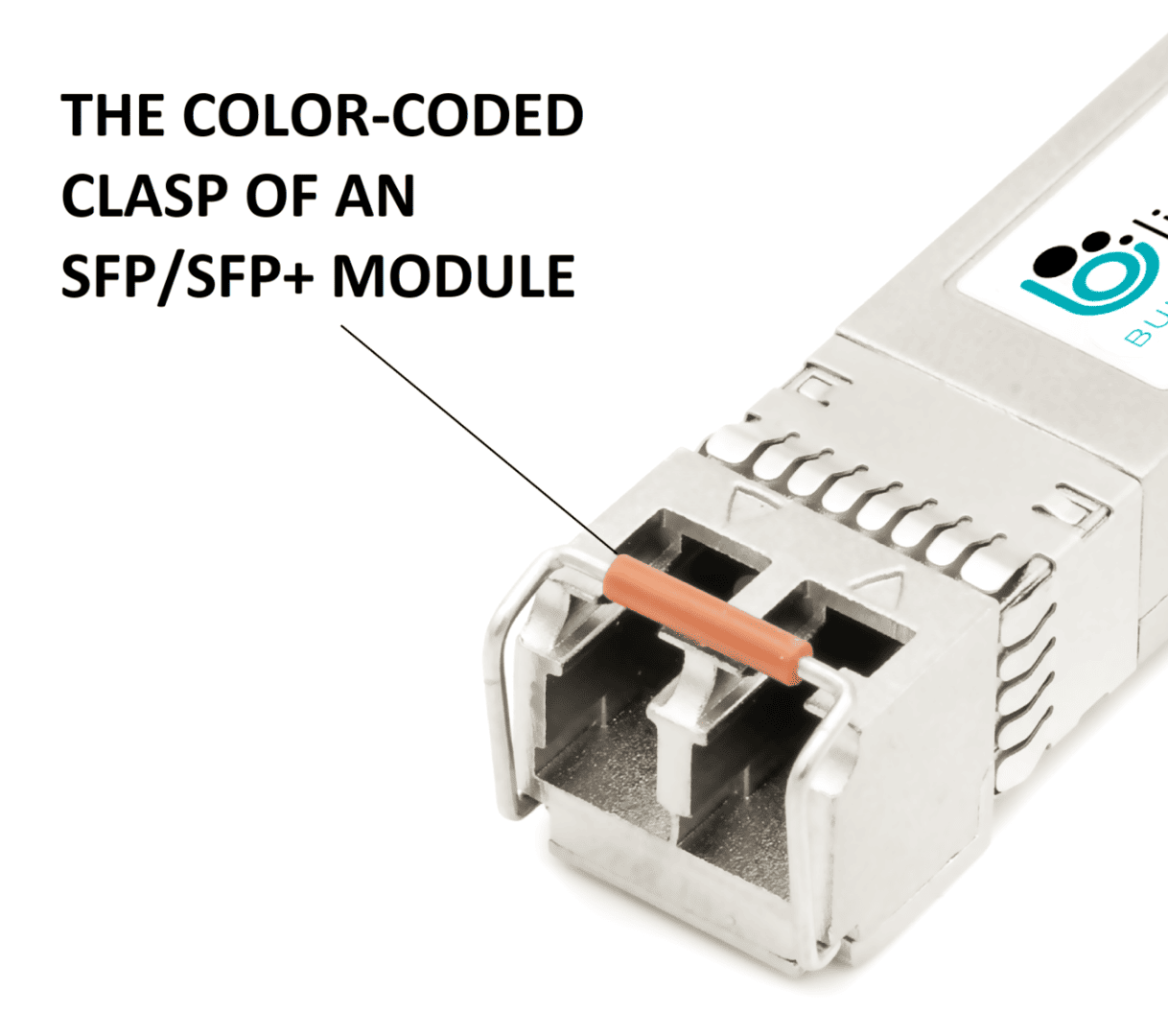
It’s important to note that the colors of clasps of SFP modules are not standardized, however, most manufacturers use similar colors for the most common SFP and SFP+ module types.
WHAT ARE THE MOST COMMON SFP TYPES AND HOW ARE THEY COLOR-CODED?
1Gbs SFP SX
- clasp color: black
- optical module: multimode MMF
- wavelength: 850 nm
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 550 m
1G SFP LX
- clasp color: blue
- optical module: single-mode SMF
- wavelength: 1310 nm
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 20 km
1G SFP EX 1310 nm
- clasp color: blue
- optical module: single-mode SMF
- wavelength: 1310 nm
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 40 km
1G SFP EX 1550 nm
- clasp color: green
- optical module: single-mode SMF
- wavelength: 1550 nm
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 40 km
1G SFP ZX
- clasp color: green
- optical module: single-mode SMF
- wavelength: 1550 nm
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 80 km
1G SFP BiDi/WDM TX 1310nm
- clasp color: blue
- optical module: single-mode SMF
- wavelength: Tx 1310nm, Rx 1550 nm
- connection: 1xLC/UPC simplex or 1xSC/UPC simplex
- distance: 3 km, 20 km, 40 km, 80 km (depending on the type of SFP module)
1G SFP BiDi/WDM TX 1550nm
- clasp color: green (gold orviolet)
- optical module: single-mode SMF
- wavelength: Tx 1310nm, Rx 1550 nm
- connection: 1xLC/UPC simplex or 1xSC/UPC simplex
- distance: 3 km, 20 km, 40 km, 80 km (depending on the type of SFP module)
100BASE-T SFP RJ45
- clasp color: gold or gold
- optical module: copper
- connector: RJ45
- distance: 100 m
100BASE-CWDM SFP
- clasp color: purple, blue, green, brown,
pink, beige, white, gray, black, orange,
red. There is no rule on the use of
a specific color
for a specific wavelength. - optical module: single-mode
- wavelength: 18 wavelengths from 1270 nm to 1610 nm (with a gap of 20 nm)
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 40 km, 80 km, 100 km, 120 km (depending on the type of module)
100BASE-DWDM SFP
- clasp color: there is no fixed rule for using a specific
color for each DWDM channell, each manufacturer uses
its own clasp color. - optical module: single-mode
- number of transmissionóchannels: 48 channelsóin 100 GHz mesh with 0.8 nm spacing
- connection: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 40 km, 80 km, 100 km
Types of SFP+ 10G modules
The colors of SFP+ connector clasps for some models are different from those used for SFP modules.
10G SFP+ SR
- clasp color: black
- optical module: multimode MMF
- wavelength: 850 nm
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 300 m
10G SFP+ LR
- clasp color: blue
- optical module: single-mode SMF
- wavelength: 1310 nm
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 10 km or 20 km
10G SFP+ ER
- clasp color: maroon
- optical module: single-mode SMF
- wavelength: 1550 nm
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 40 km
10G SFP+ ZR
- clasp color:white
- optical module: single-mode
- wavelength: 1550 nm
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 80 km
10G SFP+ BiDi/WDM TX 1270nm
- clasp color:gray, black-green
- optical module: single-mode
- wavelength: TX 1270 nm, RX 1330 nm
- connector: 1xLC/UPC simplex
- distance: 10 km, 20 km, 40 km, 60 km (depending on the type of module)
10G SFP+ BiDi/WDM TX 1330nm
- chuck color: blue, aqua
- optical module: single-mode
- wavelength: TX 1330 nm, RX 1270 nm
- connector: 1xLC/UPC simplex
- distance: 10 km, 20 km, 40 km, 60 km (depending on the type of module)
10GBASE-T SFP+ RJ-45
- clasp color: gold or gold
- optical module: copper
- connector: RJ45
- distance: 20 m, 30 m, 80 m
10BASE-CWDM SFP+
- clasp color:
- purple, blue, green, brown,
pink, beige, white, gray, black, orange,
red. There is no rule about the use of a particular color for a particular wavelength. - optical module: single-mode
- wavelength: 18 wavelengths from 1270 nm to 1610 nm (with a gap of 20 nm)
- connector: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 40 km, 80 km, 100 km, 120 km
10BASE-DWDM SFP+
- clasp color: there is no fixed rule for using a specific
color for individual DWDM channels, each manufacturer uses
its own clasp colors. - optical module: single-mode
- number of transmission channels: 48 channels in 100 GHz mesh with 0.8 nm spacing
and 96 channels in 50 GHz mesh with 0.4 nm spacing - connection: 2xLC/UPC duplex
- distance: 40 km, 80 km, 100 km, 120 km
SFP vs SFP+ main differences
SFP and SFP+ have identical housing dimensions but differ in data transmission speed, and transmission distance.
Transmission speed:
- The SFP module supports speeds: from 100 Mbs to 4.25 Gbs
The SFP module supports standards: Fast Ethernet 100 Mbs, Gigabit Ethernet 1 Gbs, Fiber Channel 1 Gbs, 2Gbs, 4Gbs, SONET, SDH.
- The SFP+ module supports speeds: from 6 Gbs to 32 Gbs
The SFP+ module supports standards: 10 Gigabit Ethernet, Fiber Channel 8/16/32 Gbs, SDH, OTN OTU2.
Transmission distance:
- The SFP module transmits data over a distance of up to 200 km.
- The SFP+ module transmits data over a distance of up to 80 km.
SFP vs. SFP+ What is the difference between the SFP and SFP+ modules?
The SFP and the SFP+ are identical in terms of size but differ in data transmission speed and range.
Data transmission speed
- The SFP module: from 100Mbs up to 4,25Gbs
Supported standards: Fast Ethernet 100Mbs, Gigabit Ethernet 1Gbs, Fiber Channel 1Gbs, 2Gbs, 4Gbs, SONET, SDH
- The SFP+ module: from 6Gbs up to 32Gbs
Supported standards: 10 Gigabit Ethernet, Fiber Channel 8/16/32Gbs, SDH, OTN OTU2.
Data transmission range
- SFP module: up to 200km
- SFP+ module: up to 80km
Can an SFP module work in an SFP+ port?
The SFP and SFP+ modules are identical in terms of size (WxDxH: 13,4 mm x 56,5 mm x 8,5 mm), so theoretically it is possible to insert both transceivers in the same port of a switch, converter, or server. However, whether an SFP module will work in an SFP+ port (or an SFP+ module in an SFP port) depends on the configuration of the device. Before inserting the module, make sure that your switch, server, or another networking device supports the given module in the documentation of the device.